|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reasearch field: Electric Vehicles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Development of components and systems for road and industrial electric traction |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Power electronics converters for ac traction motors |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
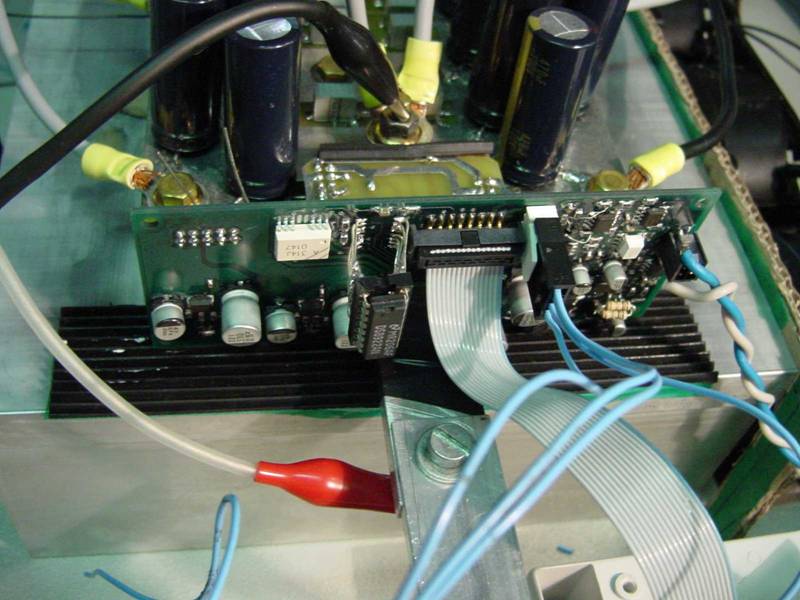
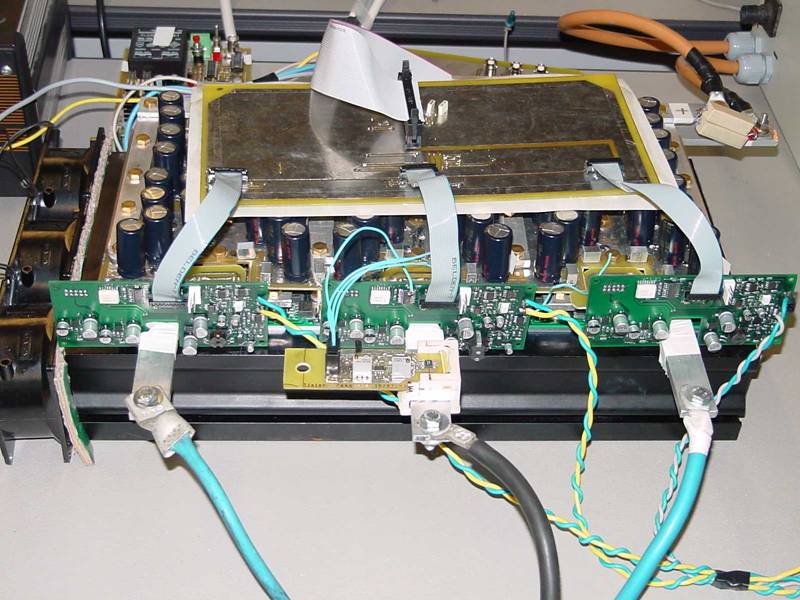
Main features of converters under development are:
-
Power stage built using IMS (Insulated Metal Substrate)
technology. Static switches are made of several Mosfets shunt connected
each other |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
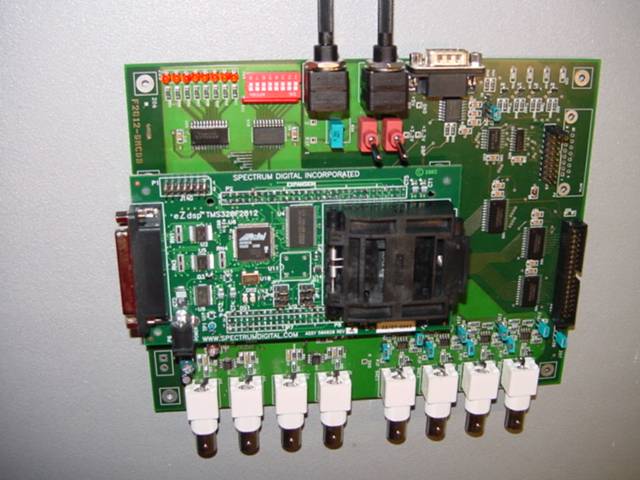
Control board for ac traction drives is characterised by:
-
single processor board, based on a last generation DSP (TMS 320F28
family);
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Development of ac motor designed specifically for traction |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three- phase induction motors: An induction machine has been designed in order to satisfy stringent requirements of volume and weight of an electric vehicle traction system. Main characteristic of the machine are:
-
electric motor mounted in the same housing of the differential
gears. This machine is able to withstand heavy stresses like vibrations, thermal shocks, powders, etc which are present in the bonnet. Electrical characteristic of the induction machines realized for VIVI vehicle are shown in the table. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Synchronous motors A new research field, regarding the development of new types of electric drives for traction, based on synchronous motors, has been activated. Both permanent magnet motors and wound-excited synchronous motor have been considered. Now the activity is focused on salient pole, wound-excited synchronous motor and its drive system. This kind of motor should be able to generate very high torque at low speed and to reach very high rotating speed. The high efficiency of the drive extends the operating range of a battery powered vehicle. The development of the wound-excited synchronous motor is targeted to realize a powerful electric traction system for industrial lift trucks and, in particular, those for very heavy loads. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
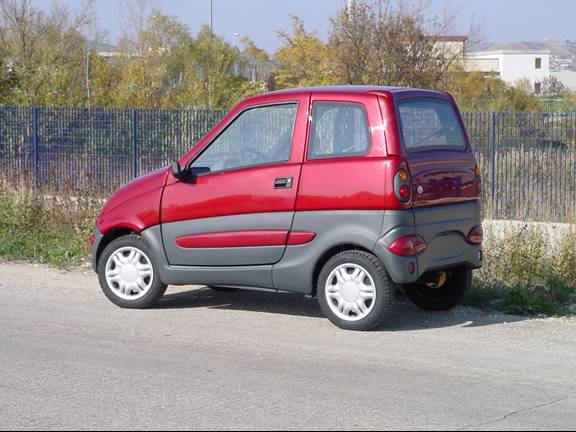
Development of Electric Vehicles |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Electric GIG |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A
project intended to improve the environmental quality of these places must
join the particular requirements of the final application. The vehicle
requirements may be summarized as follows: low emission of exhausts and
noise, small overall dimensions, large load capability, wide sight for
passengers, good climbing performance, high autonomy and inexpensive
maintenance. The Electric Gig satisfies all these stringent requirements.
This vehicle is based primarily on the use of the state of the art
technologies for batteries and drives. Furthermore, a particular shape for
the body has been adopted.
The characteristics of the proposed EV
called Electric Gig are: 3-phase water cooled induction motor, electric
drive based on a sensorless Stator Flux Vector Control (SFVC) technique,
Nickel-Sodium-chloride battery pack, efficient fitting of electric parts
in the chassis and light convertible body.
The Electric Gig has been assembled by Micro-Vett S.r.l. on the basis of a chassis of the Porter Piaggio. The design of the body has been reviewed by the Italian car designer “Vernagallo”. Up to seven passengers can accommodate on the vehicle. The electric motor has been directly coupled to the differential gearbox driving the rear wheels. The battery pack is located under the flatcar avoiding the loss of payload volume availability. The new type of battery employed (Ni-Na-Cl) allows a range above 100 Km. The power conversion unit is also located in the flatcar in the rear part of the vehicle. The high performance of the vehicle in terms of maximum speed, maximum climbing slope, and autonomy as well as the winning body design, should satisfies the market requirement providing the basis for the industrialization of this product. The Electric Gig has been built thanks to a research project financed by the Italian ministry of University and Research. The Electric Gig was presented at the Motor Show ’99 in Bologna. The Electric Gig is a prototype realized jointly by the Department of Electrical Engineering of University of Bologna and the Department of Electrical Industrial Engineering of the Polytechnic of Torino together with two private companies: Microvett s.r.l. and Elettronica Santerno S.p.A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
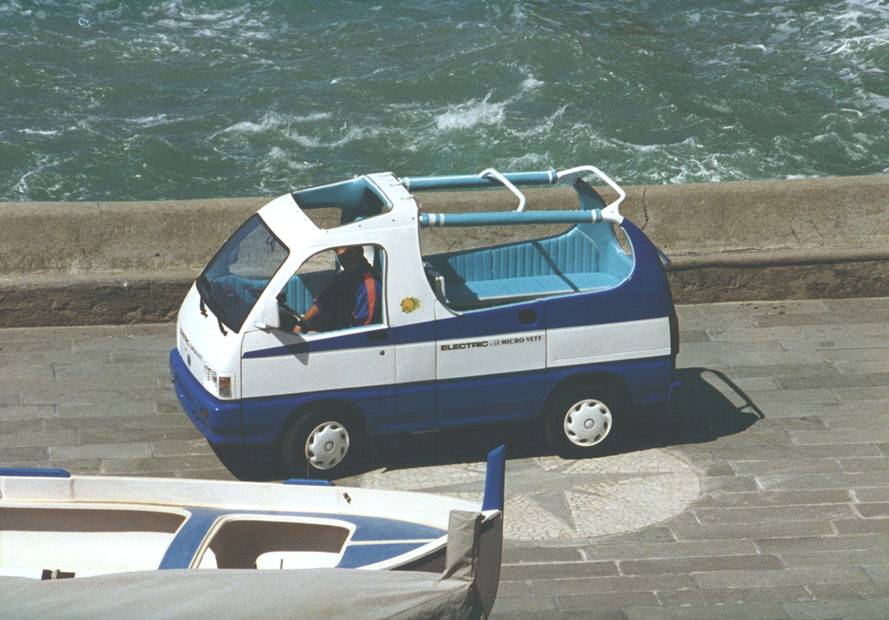
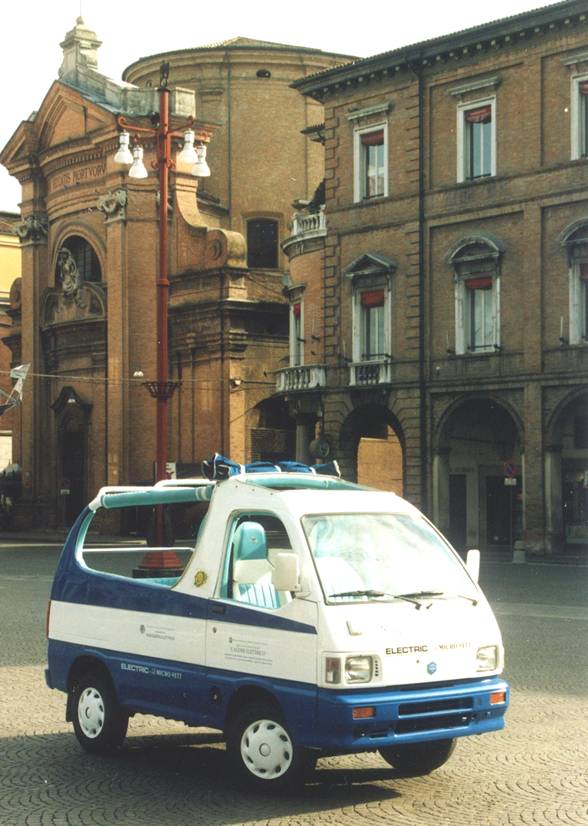
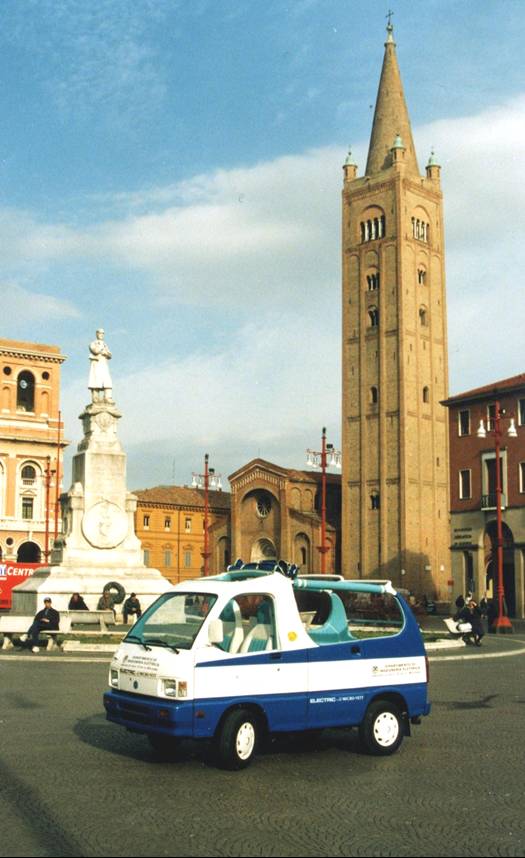
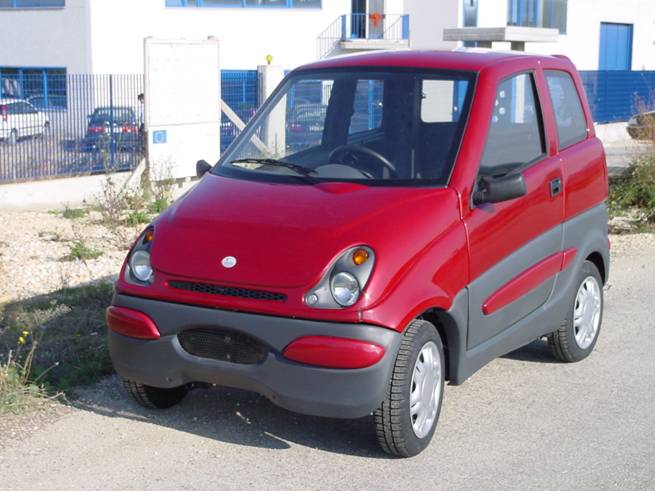
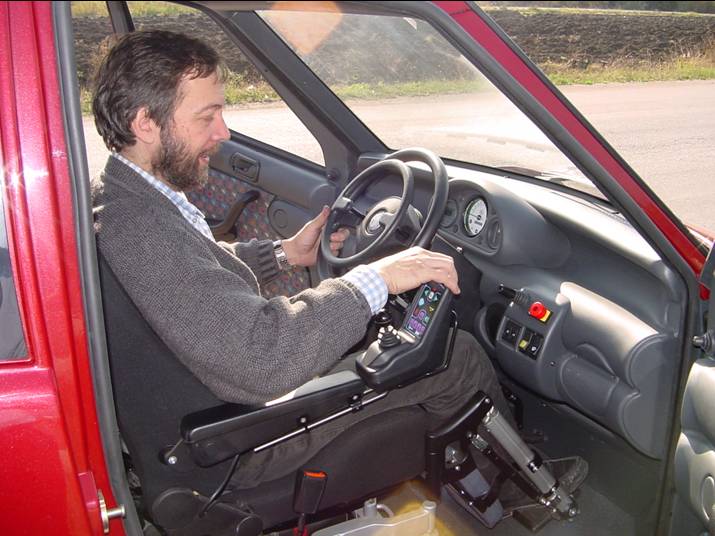
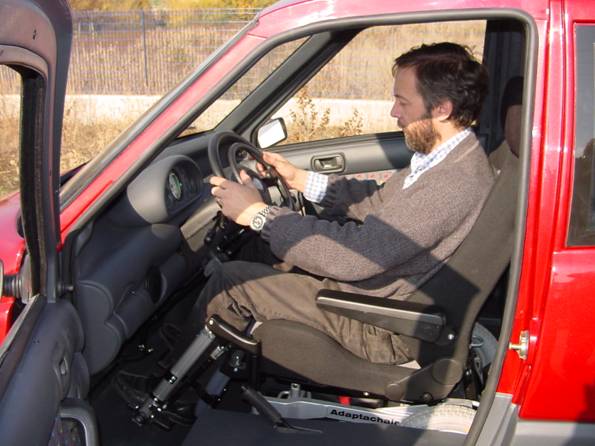
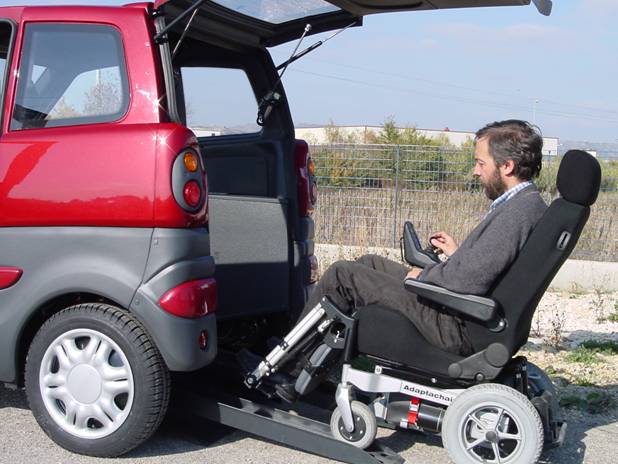
VIVI |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
VIVI (Innovative Vehicle for an
Independent Life) is a vehicle designed to satisfy the mobility needs
of handicapped peoples on wheelchair that are not able to reach by
themselves the drive seat of a car. VIVI allows handicapped people to enter inside the vehicle and to reach autonomously the drive seat position directly with their wheelchair. Then the driver utilizes drive commands at the steering wheel and circulates on urban roads.
Electric
traction is intended in order to simplify the driving, to reduce urban
pollution and to allow the vehicle circulation in limited traffic area
(city centers, pedestrian area, courtyards, ..). Main characteristic of the vehicle are:
-
automatic back door and automatic ramps with very slow slope VIVI has been realized inside the Italian research project VEMAD, financed by the Italian ministry of University and Research. The realization of this vehicle is possible thanks to a number of industrial partners and no-profit organizations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||